Mosquitoes
- Life Cycle:
- Mosquitoes undergo complete metamorphosis, consisting of four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
- Female mosquitoes lay their eggs in water, and the eggs hatch into larvae.
- Larvae go through several molts before entering the pupal stage.
- The pupa eventually emerges as an adult mosquito.
- Habitat:
- Mosquitoes breed in standing water, including ponds, puddles, marshes, and containers with stagnant water.
- Different species of mosquitoes have specific preferences for breeding sites.
- Feeding Habits:
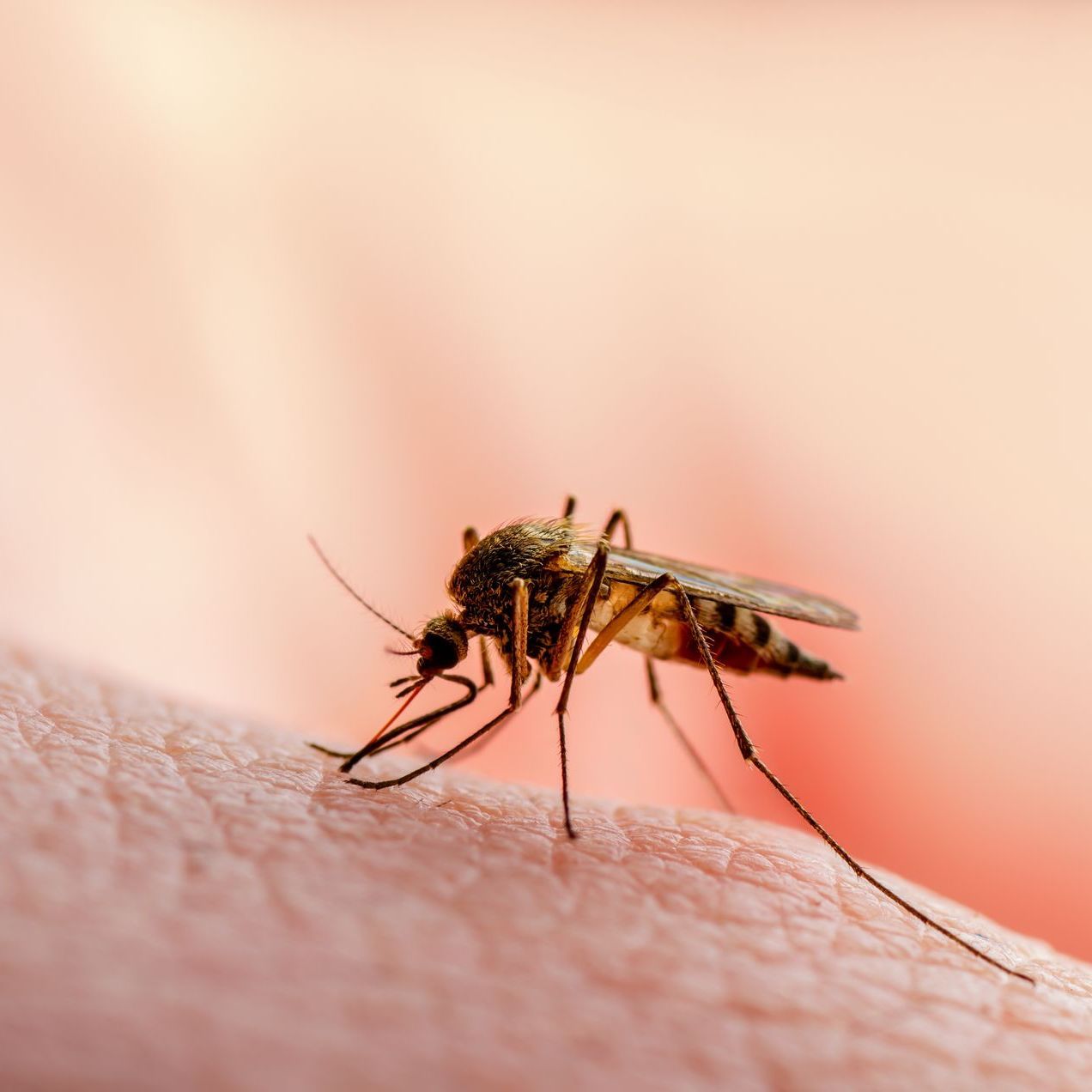
- Female mosquitoes require blood meals for the development of their eggs.
- Male mosquitoes primarily feed on nectar and plant juices and do not typically bite humans or animals.
- Female mosquitoes use specialized mouthparts to pierce the skin and extract blood.
- Disease Transmission:
- Mosquitoes are vectors for various diseases, including malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, West Nile virus, and others.
- Disease transmission occurs when an infected mosquito bites a person or animal, introducing the pathogen into the bloodstream.
- Prevention and Control:
- Preventing mosquito bites is crucial in areas where mosquito-borne diseases are prevalent.
- Use insect repellents, wear long sleeves and pants, and use bed nets to reduce exposure.
- Eliminate standing water around homes to reduce mosquito breeding sites.
- Insecticides, larvicides, and mosquito nets are used for mosquito control in various settings.
- Attractants:
- Mosquitoes are attracted to carbon dioxide, body odor, heat, and certain chemicals emitted by the skin.
- Dark clothing and certain scents can also attract mosquitoes.